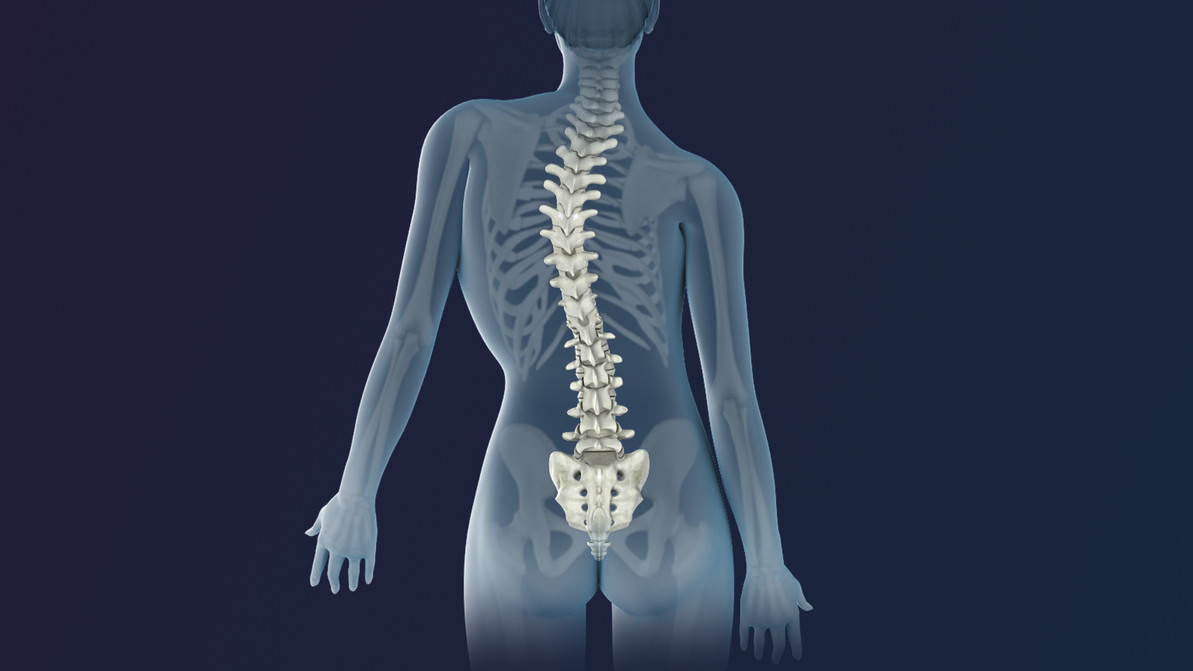
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine. This condition is not diagnosed often in adults, but most often it is diagnosed in childhood or in adolescence. Scoliosis can occur in people with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most childhood scoliosis is unknown.
The normal curves of the spine occur at the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions in what is called the sagittal plane. The purpose of these curves is to position the head over the pelvis which helps to provide shock absorption to distribute mechanical stress during movement. Scoliosis often is defined as spinal curvature in the coronal (frontal) plane. Even though the degree of curvature is measured on the coronal plane, scoliosis is a more complex three-dimensional issue that involves other planes as follows:
- Coronal Plane: This is a plane that is vertical from head to foot and parallel to the shoulders, dividing the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections.
- Sagittal Plane: Also called the longitudinal plane is plane divides the body into right and left halves.
- Axial Plane: Also called the transverse plane is a plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts. It is parallel with the ground which puts it at a right angle with the coronal plane
Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some cases can become worse as children grow. Because severe scoliosis can be disabling, children who are diagnosed with minor cases are monitored closely with X-rays to track changes as they grow. In many cases no treatment is needed. Children who need treatment will most likely need a to wear a brace to stop the curve from getting worse. Others may need surgery to straighten the severe curves.
Scoliosis affects 2-3 percent of the population which comes out to about six to nine million people in the United States. The primary age of onset for scoliosis is around 10-15 years of age for both genders.
Types of Scoliosis
There are three types of scoliosis, they are as follows:
- Idiopathic: Is the diagnosis when all other causes are excluded and comprises about 80 percent of all cases. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type of scoliosis and is usually diagnosed during puberty.
- Congenital: Is the result of embryological malformation of one or more vertebrae and may occur in any location of the spine. This type of scoliosis can be detected at a young age because abnormalities are present at birth. The geometry and location of the abnormalities determine the rate at which the scoliosis progresses in magnitude as a child grows.
- Neuromuscular: This is scoliosis that is secondary to neurological or muscular diseases. This includes scoliosis that is associated with cerebral palsy, spinal cord trauma, muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy and spina bifida. This type of scoliosis often progresses more rapidly than idiopathic scoliosis and often requires surgical treatment.
Scoliosis Symptoms
There are several symptoms that may indicate the possibility of scoliosis.They are:
- Shoulders are uneven - one or both shoulder blades may stick out.
- One or both hips are raised or unusually high.
- Head is not centered directly above the pelvis.
- Waist is uneven.
- Rib cages are at different heights.
- The entire body lens to one side.
- A prominence on one side of the back when bending forward.
- The appearance of texture of the skin overlying the spine changes (dimples, hairy patches, color abnormalities).
If one or more of these symptoms is evident, an appointment with a doctor should be scheduled. One thing to keep in mind is that scoliosis does not cause pain and can appear gradually. Because of this scoliosis often goes undetected by parents. Those who usually are the first to notice scoliosis in a child are teachers, friends, and sports teammates.
What Causes Scoliosis?
Medical professional are not sure what causes the most common types scoliosis, but it appears to be hereditary, because the disorder runs in families. Less common types of scoliosis may be caused by:
- Birth defects affecting the development of the bones and spine.
- Certain neuromuscular conditions, such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
- Injuries to or infections of the spine.
- Previous surgery on the chest wall as a baby.
- Spinal cord abnormalities.
Scoliosis Risk Factors
The risk factors for the most common type of scoliosis are:
- Age: Signs and symptoms typically begin in adolescence.
- Sex: Even though boys and girls develop mild scoliosis at the same rate, girls have much higher risks of the curve worsening and requiring treatment.
- Family History: Scoliosis can run in families.
Scoliosis Complications
Most people who have scoliosis have a mild form of it. But some complications may arise, such as:
- Back problems: Adults who had scoliosis as a child may be more likely to have chronic back pain as adults, especially if their abnormal curves are large and untreated.
- Breathing problems: In sever scoliosis, the rib cage may press against the lungs which makes it more difficult to breathe.
- Appearance: As scoliosis progresses and worsens, it can cause more noticeable changes - like uneven hips and shoulders, prominent ribs, and a shift of the waist and tank to the side.
Scoliosis Meters
Medical professionals who work to diagnose scoliosis will often use scoliosis meters to measure the degree of rotation of an abnormality of the back. We at Rehab Therapy Supplies carry scoliosis meters for medical professionals to purchase.
Related Blog Posts:
Sit and Reach Test - Flexibility Test
Using an Inclinometer for Spinal Assessments
Recent Posts
-
Acupuncture vs. Dry Needling: What’s the Difference?
At first glance, acupuncture and dry needling might seem identical. Both involve inserting thin need …Jun 11th 2025 -
What Is Dry Needling? A Modern Approach to Pain Relief and Muscle Recovery
Chronic muscle pain, tension, and restricted movement can significantly impact your daily life, sign …Jun 11th 2025 -
The Kinetic Chain and Its Importance?
The kinetic chain is a key principle in physical therapy, referring to the way muscles, joints, and …Apr 18th 2025