Understanding the Muscular System Enhances Manual Muscle Testing with Handheld Dynamometers
 A solid understanding of the muscular system is critical for performing manual muscle testing (MMT) accurately, especially when using handheld dynamometers to measure muscle strength. By knowing how muscles function and their anatomical structure, healthcare professionals can conduct muscle tests more effectively, pinpoint weaknesses, and make informed decisions about treatment or rehabilitation. Here’s how in-depth knowledge of the muscular system supports better manual muscle testing:
A solid understanding of the muscular system is critical for performing manual muscle testing (MMT) accurately, especially when using handheld dynamometers to measure muscle strength. By knowing how muscles function and their anatomical structure, healthcare professionals can conduct muscle tests more effectively, pinpoint weaknesses, and make informed decisions about treatment or rehabilitation. Here’s how in-depth knowledge of the muscular system supports better manual muscle testing:
1. Identifying Muscle Groups and Function
To perform accurate MMT with a handheld dynamometer, you need to first identify the specific muscle or group of muscles being tested. For example:
- Biceps Brachii: Responsible for elbow flexion, testing this muscle involves positioning the patient’s arm in a bent position and applying resistance to measure strength.
- Quadriceps Femoris: The primary extensor of the knee, knowing how to isolate this muscle for strength testing is key in post-injury recovery assessments.
Understanding the origin, insertion points, and actions of muscles allows for precise test placement of the dynamometer and ensures that the test targets the correct muscle group without compensatory movement from surrounding muscles.
2. Positioning for Accurate Muscle Testing
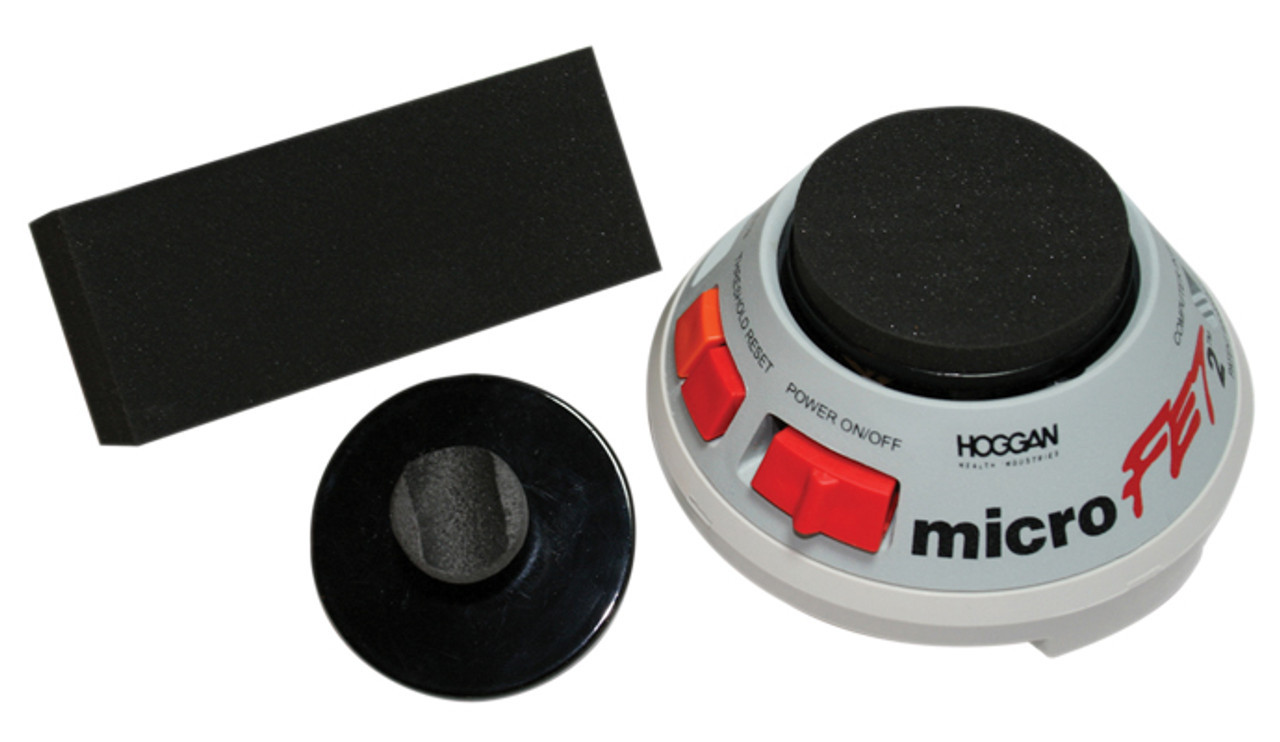
Proper body positioning is crucial when using a handheld dynamometer like the MicroFET 2 or the Lafayette Hand-Held Dynamometer to ensure reliable results. Knowledge of muscle anatomy helps you position the joint in a way that isolates the muscle being tested. For example:
- When testing the gastrocnemius (a calf muscle), the patient’s leg should be positioned so that the ankle can be dorsiflexed while you apply pressure with the dynamometer during plantarflexion.
- For testing the deltoid muscle, proper positioning of the shoulder at the right angle is essential to prevent recruitment of other muscles, such as the trapezius.
Without knowledge of skeletal muscle anatomy and physiology, improper positioning can lead to inaccurate strength measurements and potentially incorrect diagnoses.
3. Assessing Muscle Contraction Types
Different muscles and tasks involve varying types of contractions:
- Concentric (muscle shortens during contraction),
- Eccentric (muscle lengthens under tension), and
- Isometric (muscle length stays the same).
Most handheld dynamometers are used to measure isometric muscle contractions, meaning the muscle is generating force without changing length. Knowing the types of contractions involved in different movements can help clinicians adjust their testing methods to gather the most relevant data.
4. Understanding Muscle Imbalances and Weaknesses
Having a detailed understanding of muscle physiology allows clinicians to better interpret the results from manual muscle testing. For instance, identifying whether muscle weakness is due to an innervation problem, muscle atrophy, or a muscle strain can inform the next steps in treatment. Furthermore, understanding agonist and antagonist muscle relationships helps in diagnosing muscle imbalances, which are common in sports injuries or post-surgery rehab.
5. Applying Targeted Resistance
Handheld dynamometers apply resistance to measure the force output of a muscle. Understanding the muscular system function ensures that this resistance is applied correctly to the muscle belly or appropriate tendon during manual muscle testing. Misplacing the dynamometer could lead to resistance being applied to other muscles, leading to inaccurate strength readings.
By having a deep knowledge of the muscular system, clinicians can perform more precise muscle strength tests, leading to more accurate diagnoses, better rehabilitation planning, and improved patient outcomes. Understanding what the muscular system does and the importance of manual muscle testing grades (or MMT grades) further enhances the effectiveness of these tests, ensuring optimal patient care.
Recent Posts
-
Acupuncture vs. Dry Needling: What’s the Difference?
At first glance, acupuncture and dry needling might seem identical. Both involve inserting thin need …Jun 11th 2025 -
What Is Dry Needling? A Modern Approach to Pain Relief and Muscle Recovery
Chronic muscle pain, tension, and restricted movement can significantly impact your daily life, sign …Jun 11th 2025 -
The Kinetic Chain and Its Importance?
The kinetic chain is a key principle in physical therapy, referring to the way muscles, joints, and …Apr 18th 2025