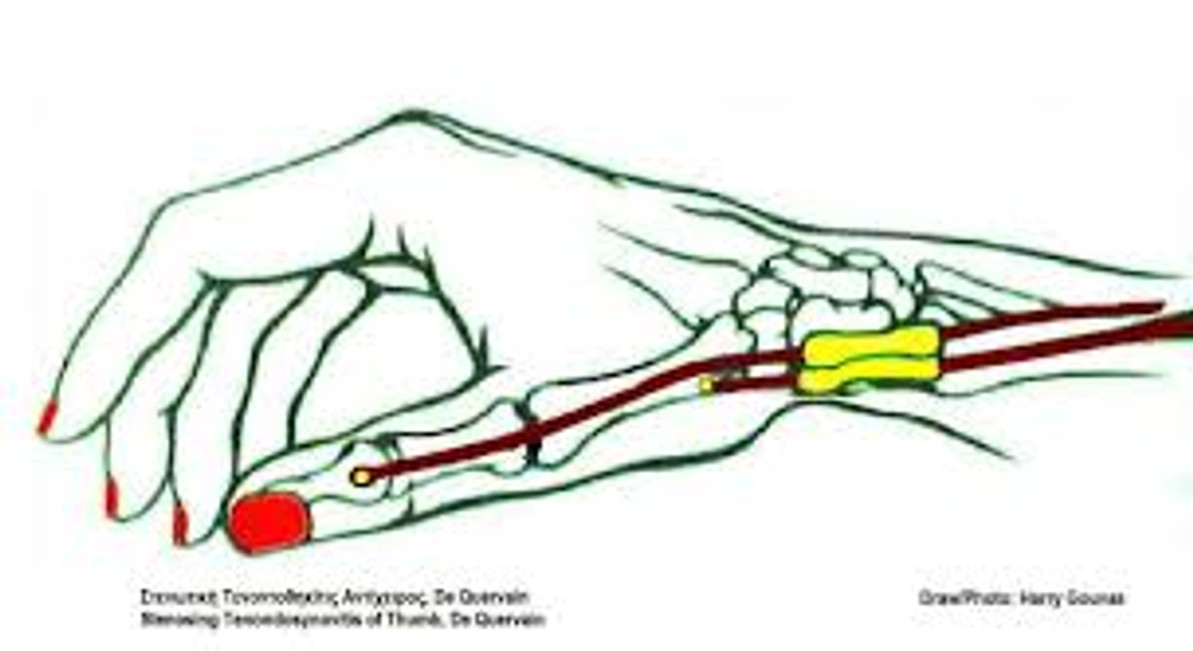
Understanding De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, though lesser-known than some other wrist conditions, can cause significant discomfort and hinder daily activities for those affected. This condition, characterized by inflammation of the tendons around the base of the thumb, often results from repetitive hand and wrist movements. However, with proper prevention and treatment measures, individuals can manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Understanding De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed or irritated, leading to pain and swelling. This condition is named after Dr. Fritz de Quervain, a Swiss surgeon who first described the condition in 1895. Inflammation typically arises from repetitive activities that involve gripping, pinching, or twisting motions of the wrist and thumb. Common causes include excessive texting, typing, gaming, gardening, or activities that involve repetitive hand and wrist movements. Additionally, certain factors such as age, gender (it's more common in women), and underlying conditions like arthritis can predispose individuals to this condition.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis involves minimizing activities that strain the tendons in the wrist and thumb. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Ergonomic Practices: Maintain proper wrist and hand positioning while typing, texting, or performing repetitive tasks. Use ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and wrist supports to reduce strain.
- Take Breaks: Incorporate regular breaks during activities that involve repetitive hand movements. Stretching exercises can help alleviate tension and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
- Modify Activities: If possible, alternate between tasks that utilize different muscle groups to prevent overuse of specific tendons. Avoid prolonged periods of repetitive thumb and wrist motions.
- Use Assistive Devices: Employ tools or devices that reduce strain on the wrist and thumb, such as voice-to-text software for typing or specialized gardening tools with ergonomic handles.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis often involves a combination of self-care strategies and medical interventions:
- Rest and Immobilization: Resting the affected hand and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help alleviate pain and inflammation. Immobilizing the thumb and wrist with a splint or brace can facilitate healing.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in specific exercises designed to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the wrist and thumb can aid in rehabilitation and prevent recurrence.
- Steroid Injections: In cases of persistent pain and inflammation, a healthcare professional may administer corticosteroid injections directly into the inflamed tendon sheath to reduce swelling and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe or refractory cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered to release the affected tendon sheath and alleviate pressure on the tendons.
Conclusion
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life, but with proper prevention strategies and prompt treatment, individuals can effectively manage this condition. By adopting ergonomic practices, modifying activities, and seeking timely medical intervention when necessary, individuals can alleviate symptoms, prevent recurrence, and maintain optimal hand and wrist health. If you suspect you may have De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis or are experiencing persistent wrist pain, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Related Blog Posts:
Texting and Typing: Navigating Wrist Pain in the Digital Age
Preventing and Managing Gamer's Wrist
Related Information:
De Quervain Tenosynovitis (Mayo Clinic)
Recent Posts
-
How Occupational and Hand Therapists Perform Initial Hand Function Evaluations
When a patient begins hand therapy—whether recovering from an injury, surgery, or neurolo …Apr 6th 2025 -
What to Expect During Hand Therapy: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers
If you’re starting hand therapy—whether after surgery, a stroke, or a neurological …Apr 6th 2025 -
Improve Hand Function and Dexterity with the Neofect Smart Pegboard
The Neofect Smart Pegboard is a revolutionary tool in the field of occupational therapy. I …Mar 25th 2025