Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Prevention and Treatment
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent and often debilitating condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm, CTS can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. However, with proactive measures and appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage and alleviate the symptoms of this condition. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, exploring strategies for prevention and outlining effective treatment modalities.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
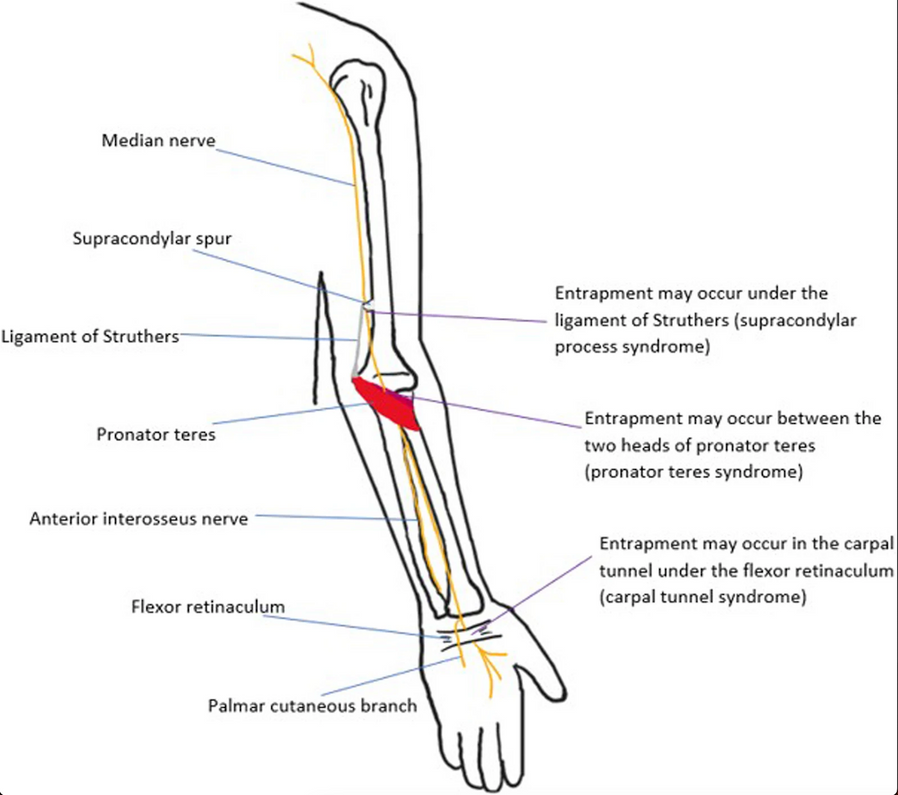
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist through which the median nerve, along with tendons, passes from the forearm to the hand. When the median nerve becomes compressed or irritated within this confined space, it can lead to the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Various factors, including repetitive hand movements, wrist injuries, anatomical predispositions, and certain medical conditions like diabetes or arthritis, can contribute to the onset of CTS.
Prevention Strategies:
- Ergonomic Workspace Setup: Maintaining proper ergonomics in the workplace is crucial for preventing CTS. Ensure that your workstation is designed to promote neutral wrist positions, with ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and adjustable chairs.
- Frequent Breaks and Stretching: Incorporating regular breaks into your work routine allows your hands and wrists to rest and recover. Perform simple stretching exercises for the wrists and fingers to alleviate tension and reduce the risk of injury.
- Use of Assistive Devices: Utilize ergonomic tools and assistive devices, such as wrist splints or padded mouse pads, to minimize strain on the wrists during activities that involve repetitive hand movements.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and excess body weight can increase the risk of developing CTS. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet can help manage weight and reduce the likelihood of CTS.
- Proper Hand Positioning: Avoid prolonged periods of wrist flexion or extension, as these positions can exacerbate pressure on the median nerve. Keep your wrists in a neutral position when typing, writing, or performing other manual tasks.
Treatment Options:
- Wrist Splinting: Wearing a wrist splint, particularly at night, can help alleviate symptoms by immobilizing the wrist and reducing pressure on the median nerve. Splinting is often recommended as a first-line treatment for mild to moderate CTS.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with CTS. However, long-term use should be monitored under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises focused on strengthening the muscles of the hand and wrist, as well as improving flexibility and range of motion, can be beneficial for managing CTS symptoms. A physical therapist can tailor a program to suit individual needs and goals.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of persistent or severe symptoms, corticosteroid injections may be administered into the carpal tunnel to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. These injections can provide temporary relief and may be combined with other treatment modalities for optimal outcomes.
- Surgery (Carpal Tunnel Release): In refractory cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended. During this procedure, the roof of the carpal tunnel is surgically divided to alleviate pressure on the median nerve, providing long-term symptom relief for many individuals.
In conclusion, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can pose significant challenges to daily functioning and quality of life, but with proactive prevention strategies and effective treatment modalities, individuals can effectively manage and alleviate its symptoms. By prioritizing ergonomics, incorporating regular breaks and stretching, and seeking timely medical intervention, individuals can mitigate the risk of CTS and maintain optimal hand and wrist health. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to receive personalized treatment and support on the journey to recovery. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing long-term complications and restoring function and comfort to the hands and wrists.
Related Blog Posts:
Preventing and Managing Gamer's Wrist
Additional Information:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease)
Recent Posts
-
How Occupational and Hand Therapists Perform Initial Hand Function Evaluations
When a patient begins hand therapy—whether recovering from an injury, surgery, or neurolo …Apr 6th 2025 -
What to Expect During Hand Therapy: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers
If you’re starting hand therapy—whether after surgery, a stroke, or a neurological …Apr 6th 2025 -
Improve Hand Function and Dexterity with the Neofect Smart Pegboard
The Neofect Smart Pegboard is a revolutionary tool in the field of occupational therapy. I …Mar 25th 2025