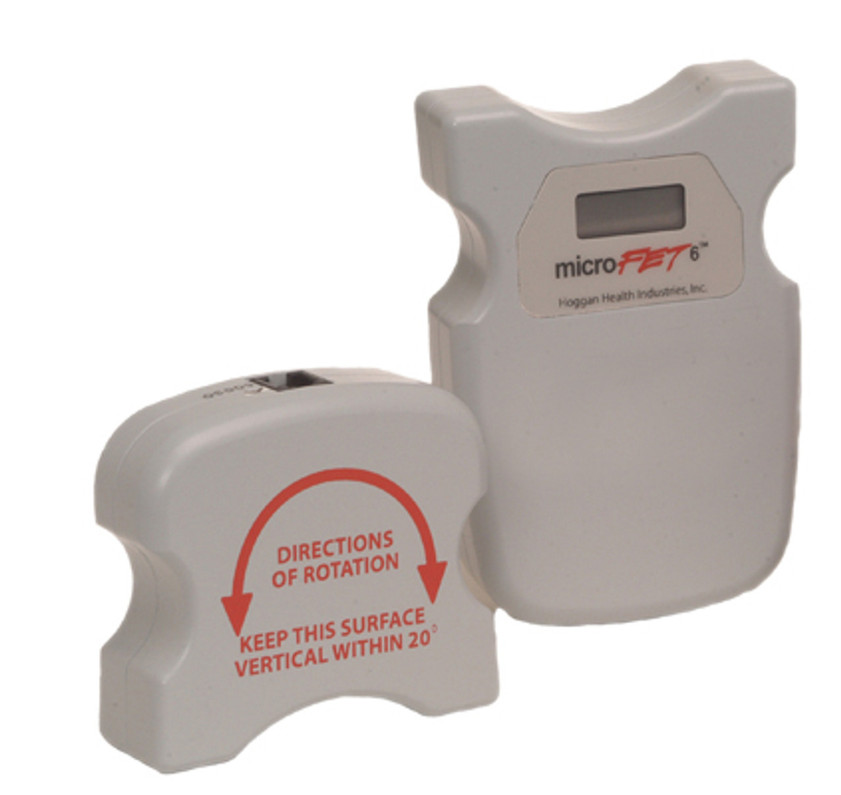
A Guide to Joint Range of Motion (ROM) Measurement Using an Inclinometer
Joint Range of Motion (ROM) measurement is a fundamental aspect of musculoskeletal assessment in various medical fields, including orthopedics, physical therapy, and rehabilitation medicine. Accurate ROM assessment provides valuable information about the flexibility, mobility, and overall health of joints. This aids in diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring progress. One of the key tools used for ROM measurement is the inclinometer, a device designed to precisely measure angles. In this guide, we'll explore the principles and techniques of conducting ROM measurements with an inclinometer.
Understanding Medical Inclinometers
A medical inclinometer is a specialized instrument used to measure angles of inclination or tilt. In the medical field, inclinometers are typically digital or analog devices with a calibrated scale, allowing for accurate angle measurement. Some inclinometers are handheld, while others are designed for attachment to body segments or specific anatomical landmarks.
 ROM Assessments with Medical Inclinometers
ROM Assessments with Medical Inclinometers
Before conducting ROM measurements with an inclinometer, it's essential to prepare both the patient and the environment. Ensure that the patient is comfortably positioned, either sitting or lying down, depending on the joint being assessed. Clear any clothing or obstructions that may interfere with the measurement process. Familiarize the patient with the procedure to ensure cooperation and relaxation during the assessment. The following are the steps for doing a ROM assessment with an inclinometer:
- Identify the Joint: Determine the specific joint or joints to be assessed. Common joints for ROM measurement include the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle.
- Position the Inclinometer: Place the inclinometer either directly on the joint's axis of rotation or on adjacent body segments, depending on the joint's anatomy and the measurement technique being employed. Ensure that the inclinometer is securely attached and aligned with the joint's motion plane.
- Establish the Zero Position: Calibrate the inclinometer to establish the zero position, ensuring accurate baseline measurement. This step may involve aligning the inclinometer parallel to the ground or using anatomical landmarks as reference points.
- Perform the ROM Measurement: Instruct the patient to move the joint through its full range of motion while keeping the inclinometer aligned and stationary. Encourage smooth, controlled movements to prevent compensatory motions or muscle guarding.
- Record the Measurements: As the patient moves the joint, read and record the corresponding angle displayed on the inclinometer at various points throughout the ROM. Note any limitations, pain, or discomfort experienced by the patient during the assessment.
- Repeat as Needed: For comprehensive ROM assessment, repeat the measurement process for each plane of motion relevant to the joint being assessed. This may include flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, internal/external rotation, and circumduction, among others.
Interpretation or ROM Assessment
Once the ROM measurements have been obtained, interpret the findings in the context of the patient's clinical presentation, functional goals, and treatment plan. Compare the measured ROM values to established norms for the patient's age, gender, and activity level. Identify any deficits, asymmetries, or restrictions in ROM that may indicate underlying pathology, joint stiffness, muscle weakness, or joint instability.
Clinical Applications
ROM measurements obtained using inclinometers have diverse clinical applications across various medical specialties:
- Diagnosis of musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, tendonitis, ligament injuries, and joint contractures.
- Treatment planning and goal setting in physical therapy and rehabilitation programs.
- Monitoring progress and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions such as exercise, manual therapy, and surgical procedures.
- Preoperative and postoperative assessment of joint function and surgical outcomes.
Joint Range of Motion (ROM) measurements with an inclinometer is a valuable tool for assessing musculoskeletal health, guiding clinical decision-making, and optimizing patient care. By accurately quantifying joint mobility and flexibility, ROM assessments help clinicians diagnose pathology, develop targeted treatment plans, and monitor progress throughout the rehabilitation process. With proper technique and interpretation, inclinometer-based ROM measurements contribute to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients across a wide range of medical conditions.
Related Blog Posts:
Using an Inclinometer for Spinal Assessments
Recent Posts
-
Acupuncture vs. Dry Needling: What’s the Difference?
At first glance, acupuncture and dry needling might seem identical. Both involve inserting thin need …Jun 11th 2025 -
What Is Dry Needling? A Modern Approach to Pain Relief and Muscle Recovery
Chronic muscle pain, tension, and restricted movement can significantly impact your daily life, sign …Jun 11th 2025 -
The Kinetic Chain and Its Importance?
The kinetic chain is a key principle in physical therapy, referring to the way muscles, joints, and …Apr 18th 2025